Vyatta is an open-source Linux distribution that offers IPv4 and IPv6 routing, as well as other features such as a stateful firewall. An .ISO can be downloaded at the link below.
The screen captures below were taken using VMware Workstation and Vyatta version 6.6. An additional network adapter was added to the virtual machine’s configuration before the initial boot.
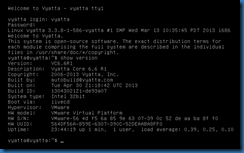
The .ISO is a Live CD that allows a direct boot. The default user name and password are vyatta. The show version command will display the version number of the application.
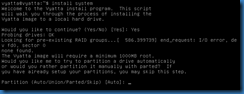
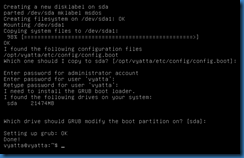
The install system command will start a wizard to install the application on the local hard drive.
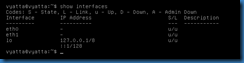
As stated above, two network adapters were installed on the virtual machine. This can be verified by the show interfaces command.
Vyatta is similar to Cisco’s IOS operating system in that it has two modes: Operational and Configuration. To enter Configuration Mode, use the command configure. To exit Configuration Mode, use the exit command. To save a change, use the commit command as well as the save command.
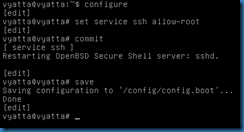
To allow SSH access, use the command set service ssh allow-root within the Configuration Mode. Commit and save the modification.
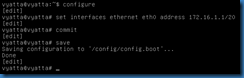
To configure an initial IP address value, use the command set interfaces ethernet ethx address x.x.x.x/x.
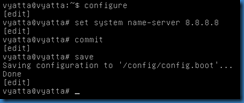
To set the DNS server value, use the command set system name-server x.x.x.x.
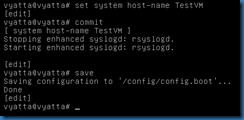
The main gateway address can be set using the command set system gateway-address x.x.x.x. The current configuration can be displayed by using the command show –all within the Configuration Mode. The command run show configuration should display the same data. The command show configuration commands should display information without the {} lines. The hostname can be set by using the command set system host-name.
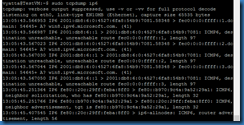
Tcpdump is available for packet analysis. To view packets for IPv6 for example, use the command sudo tcpdump ip6.
Another example would be sudo tcpdump -nvi eth0 dst 172.16.1.1 and not port 22, which would return all traffic on eth0 with a destination IP address of 172.16.1.1 when the port is not 22.
The application tshark is available as well.
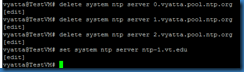
Several default time servers are present. The command delete system ntp server value can be used to remove the default entries, and set system ntp server value can be used to add a new entry.
To shutdown the operating system, use the command poweroff.
A site that includes more commands can be found at http://www.v12n.com/mediawiki/index.php/Vyatta_How_To. Details concerning IPv6 commands can be found at http://samsclass.info/ipv6/proj/pV7-dhcpv6.html.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.