StarWind Converter is a free downloadable V2V conversion tool for virtual machines. You can use it to convert VMDK to VHD files and VHD to VMDK. It is a sector by sector copy operation from one format to the other. It does not modify the source image and will leave it so you can continue to use it.
Thursday, May 3, 2012
Apropos Command
The apropos command within Ubuntu searches the available man pages for the phrase in question. For example, the command apropos network will return man pages that contain the string “network”. The apropos command is the same as using man –k.
Sandcat Browser
Sandcat Browser is a freeware portable pen-test oriented multi-tabbed web browser with extensions support developed by the Syhunt team. The Sandcat Browser is built on top of Chromium, the same engine that powers the Google Chrome browser, and uses the Lua language to provide extensions and scripting support.
Wednesday, May 2, 2012
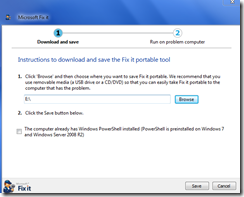
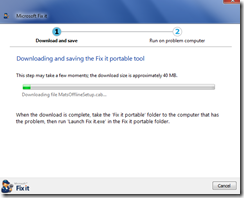
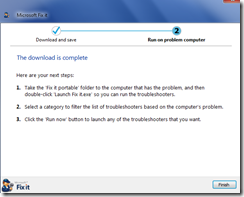
Microsoft Portable Fixit Utility
Microsoft has produced several Fixit executable files that solve particular issues such as audio playback. A new portable version has been released that includes multiple solutions. The initial installer can be found at:
http://go.microsoft.com/?linkid=9775982
Below are some of the screens during the installation. The initial installer application will ask for a destination path, and then download the rest of the components.
If the final executable is launched, a main menu should appear with the various options that can be used.
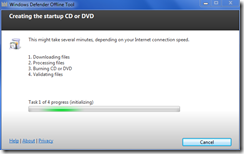
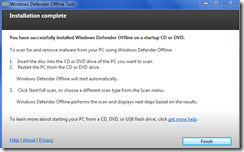
Windows Defender Offline
Windows Defender Offline is a malware tool from Microsoft for use with a bootable USB or CD/DVD disk. It is similar to bootable tools from other security vendors. The download to the 32-bit and 64-bit versions can be found at:
http://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows/what-is-windows-defender-offline
Below are some screen captures of the utility in use.
Tuesday, May 1, 2012
AxCrypt
AxCrypt is the leading open source file encryption software for Windows. It integrates seamlessly with Windows to compress, encrypt, decrypt, store, send and work with individual files. Right-click integration with Windows Explorer makes AxCrypt the easiest way to encrypt individual files in Windows.
IPv6 General Information
Below is some general information concerning IPv6. With IPv4, the "class" of an address can be figured out by the first octet. For example:
CLASS A (0.0.0.0 through 126.255.255.255)
CLASS B (128.0.0.0 through 191.255.255.255)
CLASS C (192.0.0.0 through 223.255.255.255)
CLASS D (multicast 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255)
CLASS E (experimental 240.0.0.0 through 255.255.255.255)
In IPv4 there are special addresses:
Loopbacks (127.0.0.0 through 127.0.0.255
RFC 1918 private addresses (10.x.x.x, 172.16-31.255.255, 192.168.x.x)
DHCP services not available (169.254.x.x)
With IPv6 the first several bits describe an IP address "TYPE". (remember we are talking about the first couple of "bits" in the address) For example:
010 - Unicast addresses for service provider allocation (4000::0 through 5FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF)
100 - Geographic IP addresses (8000::0 through 9FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF)
1111 1110 10 - link local addresses (FE80::0 through FEBF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF)
1111 1110 11 - site local addresses (FEC0::0 through FEFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF)
1111 1111 - multicast addresses (FF00::0 through FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF)
IPv6 has some special addresses:
0::0 - unspecified
0::1.1.1.1 through 0::255.255.255.255 - IPv4 addresses
0::0001 - loopbacks
IPv6 stacks will perform an auto-configuration if no router or DHCPv6 service is present. This is similar to the 169.254.*.* value assigned via Automatic Private IP Addressing with IPv4. The beginning value will be fe80 such as the example below:
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::d0ce:643:c4df:a825%20(Preferred)
The current value beginning values for an IPv6 address would be 2001, 2002, or 2003. Both the addresses listed below are public addresses: ![]()
If the "stateless" method is used to determine the IPv6 value, the string of FF:FE will be present at the same location: ![]()
The default method of creating a IPv6 address for some operating systems is to include the MAC address value from the adapter. In the example below, the client has been configured not to use this method:
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-21-70-B5-A1-50
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::f0f4:13c4:3427:885c%12(Preferred)
The normal configuration method for IPv6 is to configure a router to "advertise" the details required. Below is a capture of a router advertisement packet: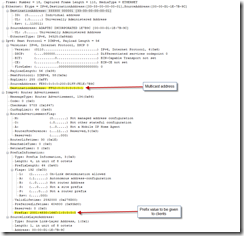
The Multicast address of FF02::1 is normally used for a router advertisement. The example packet below shows a Neighbor Solicitation broadcast. The Neighbor Solicitation message allows a device to check that a neighbor exists and is reachable, and to initiate address resolution.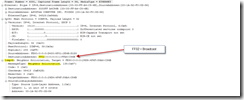
Below is an example of a packet using IPv6 and the Link Local Multicast Name Resolution.
The packet below is another IPv6 example. MLD is used by an IPv6 router to discover the presence of multicast listeners on directly attached links, and to discover which multicast addresses are of interest to those neighboring nodes.
A neighbor advertisement message is sent to inform other hosts of a Mac Address to IP address relationship. These messages can be sent in response to a request, or unsolicited as a host comes online. The flags parameters are:
R-Router -> Set if sender is a router
S-Solicited -> Set if this is a response to a Neighbor Solicitation Message
O-Override -> Advertisement overwrites existing cache

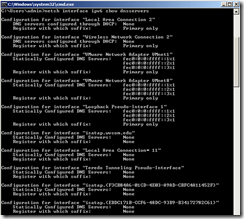
To disable the Teredo component with Windows, use the command "netsh interface teredo set state disabled". To disable IPv6 within the Registry, access HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\tcpip6\Parameters\. Create a DWORD value with the name of DisabledComponents. To disable IPv6 on all interfaces, use FFFFFFFF. So the final string would be:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\TCPIP6\Parameters]
"DisabledComponents"=dword:ffffffff
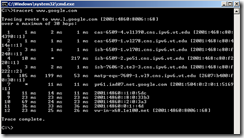
Below are some examples of parameters obtained while on the campus of Virginia Tech, which has used IPv6 for some time.