W3Perl is a free logfile analyzer for Web / FTP / Squid / CUPS and Mail servers. The perl scripts can analyze logfiles and can produce HTML/PDF reports.
Thursday, April 7, 2011
Monday, April 4, 2011
Smooth-Sec
Smooth-Sec is a ready to-go IDS/IPS Linux distribution based on Suricata and Snorby. It's possible to deploy a complete IDS/IPS System up and running out of the box within a few minutes, even for security beginners with minimal Linux experience.
Saturday, April 2, 2011
Click to Play feature within Google Chrome
Google Chrome has a “Click to Play” feature to allow selective usage of plug-ins. The screen captures below were taken with Chrome version 10.
Launch Chrome and enter the URL about:flags. This should display a list of experimental features. Click on the Enable link under the Click to Play section.
Restart the browser. Click on Options, Under the Hood, and then the Content Settings button. Under the Plug-ins section, a third option should be present for Click to Play.
Plug-ins such as Flash should now require a click before loading.
ActiveX Filtering with Internet Explorer 9
Internet Explorer 9 includes a new security feature named ActiveX Filtering. This component allows global or selective blocking of ActiveX controls.
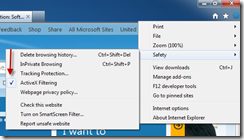
This option is off by default. To enable it, click on the Tools icon, Safety, and then ActiveX Filtering. No configuration text or dialog box will be displayed. Access the same path and verify that a check mark is present to the left of the menu option.
If a site is accessed that has an ActiveX control that was blocked, the icon that resembles a blue circle with a line through it within the address bar will display the the text of “Some content is filtered on this site” when the cursor is placed on it.
Some web sites will display warnings that the control is question is not available for use.
If you click on the icon that resembles a blue circle with a line through it, a small dialog box will appear which will allow access on the site in question.
The text within the dialog box can be misleading in clicking the button does not turn off ActiveX Filtering globally, but only for the current web site. If the site is added, the normal notification at the bottom of the screen should appear.
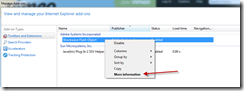
To view the list of sites that have been allowed, click on the Tools icon and then Manage Add-ons. Right-click on the entry under the Toolbars and Extensions area and click on the More Information option.
The dialog box should display a list of sites that have been added as an exception. A button is also available to enable the control in question across all sites. For example, ActiveX Filtering could be enabled but Flash could be allowed for all sites.
Introduction to VMware Resource Allocation
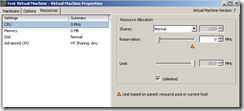
Below is some basic information concerning resource allocation for virtual machines within a VMware environment.
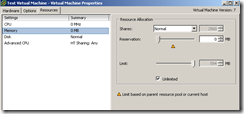
The memory reservation amount specified on the Resources tab of the virtual machine settings is the amount of actual physical memory that the ESX/ESXi host must provide. The default is 0MB, or no reservation.
For example, 512 MB of memory is set as the reservation value. This means that the VM is guaranteed 512 MB of “real” memory. If the VM is configured for 1 GB, the other 512 MB can be provided by “real” memory or the VMkernal swap file.
The Limit parameter sets the actual limit on how much physical memory may be utilized by the virtual machine. An example would be:
1. A virtual machine is configured with 1 GB of memory. So the guest OS within the VM believes it has 1 GB of memory available to use.
2. A reservation is set to 512 MB. The ESX/EXSi host must allocate 512 MB of physical memory to this VM.
3. A limit is set at 768 MB. If enough physical memory is installed and available, the hypervisor will allocate memory to the VM as needed up to 768 MB.
4. The 256 MB “gap” between the reservation and the limit may be supplied by either VMKernel swap space or physical memory.
The Shares parameter provides a means of assigning resource priority to virtual machines. If two virtual machines want more memory than their reservation limit and the ESX/ESXi host can not satisfy both of them using RAM, the share values can be used so that one gets higher-priority access to the RAM in the host.
CPU allocation is similar to memory concerning reservations and limits.
The default CPU reservation is 0MHz. By default, a virtual machine is not guaranteed any CPU activity by the VMkernel. The Limits and Shares parameters are similar to the memory options discussed above.
The general rule is every VM should be created with only a single virtual CPU. Only when a VM’s performance level dictates the need should an additional CPU be allocated. The number of cores available should also be considered. For example, an eight vCPU VM should be created only on a host with eight cores or more.
Introduction to Resxtop
Resxtop is an utility found within the vSphere CLI package. This application can be currently used with a Linux client but not with a Windows client.
Once the vSphere CLI package has been downloaded and installed within a Linux client, the utility can be started in interactive mode by entering:
resxtop –server IP address
The user name and password for the ESXi host will need to be entered. The initial interactive mode screen should then appear.
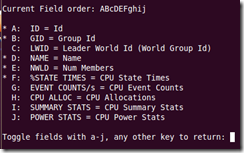
Hitting the “f” key will define the fields displayed:
When in interactive mode, the following single-key shortcuts are available:
f –> Displays a panel for adding or removing statistics columns
o –> Displays a panel for changing the order of statistics columns
q –> Quit interactive mode
c –> Switch to the CPU resource utilization panel
p –> Switch to the CPU Power utilization panel
m –> Switch to the memory resource utilization panel
n –> Switch to the network resource utilization panel
d –> Switch to the storage (disk) adapter resource utilization panel
u –> Switch to the storage (disk) device resource utilization panel
v –> Switch to the storage (disk) virtual machine resource utilization panel
i –> Switch to the interrupt panel
W –> Write the current setup to the configuration file
The utility can also be used in batch mode. To use the batch mode, run resxtop in interface mode. In each panels, select the columns you want. Save the configuration to a file by using the “W” key. Run a command such as
resxtop –server IP address –b > file.csv –n 10
Some of the flags in batch mode are:
a –> Show all statistics; this by-passes the configuration file
b –> Runs resxtop in batch mode
n –> Number of interactions
d –> Specifies the delay between statistics snapshots. The default is five seconds. The minimum is two seconds.
The batch mode can be used without the –n parameter. The utility will run until the key combination of Control + C is used. Additional information concerning this utility can be found within the VMware Resource Management Guide. The current version for ESXi version 4.1 can be found at http://www.vmware.com/pdf/vsphere4/r41/vsp_41_resource_mgmt.pdf. An appendix chapter is present concerning esxtop and resxtop.
Friday, April 1, 2011
DHCP Server address conflict parameter with Windows Server
Using the DHCP Server component within Windows Server, an option is present to attempt to detect IP address conflicts. To access this option, right-click the IPv4 node in the DHCP management console and click on the Properties selection.
Access the Advanced tab. The default value is 0; enter 1 to have the service attempt to verify the address value it is about to assign is not currently in use.
Dig for Windows
Dig is a DNS utility normally found on a Unix/Linux platform. Windows has the nslookup command, but a version of Dig is available for Windows.
To obtain a copy of Dig for the Windows platform, access http://www.isc.org/downloads and download the latest copy of BIND. Once the .ZIP file is downloaded, extract the contents to a folder. An executable should be present for Dig:
The other files besides dig.exe, dig.html, and the .DLL files can be deleted. The basic syntax of dig.exe is:
@server name type
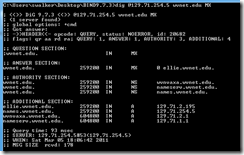
The server is the DNS server to query, the name is the domain, and the type is the DNS record to query. For example, the command below would query the DNS server at 129.71.254.5 for the MX record for the domain wvnet.edu.
dig @129.71.254.5 wvnet.edu MX
Another example of a command would be:
dig www.yahoo.com ns @129.71.254.5
The command above would query the DNS server at the IP address of 129.71.254.5 and return all name server records for the domain name of www.yahoo.com.
The option +trace returns exactly what the DNS server is going as it performs the query in question.
More options can be viewed within the dig.html help file.