Log Parser Lizard is a free GUI for the Log Parser command line utility available from Microsoft.
Sunday, March 6, 2011
TCPEye
TCPEye is a GUI alternative to the Windows netstat command. The application displays the list of all currently opened TCP and UDP ports on your local computer.
Friday, March 4, 2011
RVTools
RVTools is a windows .NET 2.0 application which uses the VI SDK to display information about your virtual machines and ESX hosts. Interacting with VirtualCenter 2.5, ESX 3.5, ESX3i, ESX4i and vSphere 4 RVTools is able to list information about cpu, memory, disks, nics, cd-rom, floppy drives, snapshots, VMware tools, ESX hosts, nics, datastores, service console, VM Kernel, switches, ports and health checks.
5nine Manager for Hyper-V
5nine Manager for Hyper-V, Free Edition, provides a local Graphical User Interface to Microsoft Hyper-V R2 server. It supports Hyper-V technology on Full and Core installations of Windows Server 2008 R2, as well as on Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 R2, which is the Microsoft's standalone free Hypervisor. You can use it when Microsoft SCVMM, or even Hyper-V Manager are not available for Core or Free versions of Server 2008 R2. It also provides Value-Add functions, such as advanced network bindings, hardware profiling and monitoring for both Free/Core and Full Hyper-V installations.
Thursday, March 3, 2011
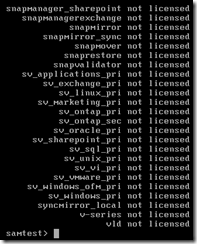
NetApp Data ONTAP general commands
Below are some examples of some general commands for the command-line interface of a NetApp Data ONTAP operating system. The screens below are from version 8.
The options command has several different parameters for configuring different parameters. For example, the command options ssh.port will display the current listening port that the SSH service is using.
If a value is entered after the command, the value is changed.
The command options trusted.hosts displays the hosts that are allowed administrative access. The default is *, which is all hosts.
The secureadmin command can change parameters such as disabling SSH, as well as displaying current configurations.
The version command will display the current version; the –b displays the version on the boot device.
The license command will display current license codes.
The config dump command saves the system configuration into a single file with the file name specified at the default path of /etc/configs. If the file already exists, the –f flag must be used.
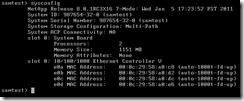
The sysconfig command displays information about the system’s hardware configuration. The –A flag will display all reports.
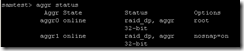
The aggr status command displays a summary of aggregate states.
The vol status command is similar but for volumes.
The netstat and netdiag commands offer assistance with the current network status of the system.
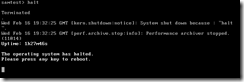
The halt command shuts the system down.
Wednesday, March 2, 2011
Microsoft Exchange RPC Extractor
The Microsoft Exchange RPC Extractor is a command-line tool that can parse network captures and interpret remote procedure calls made from a client to Microsoft Exchange.
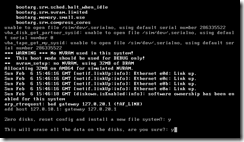
NetApp ONTAP Simulator
The NetApp ONTAP Simulator is a pre-built VMWare image that can be used for testing. In this example, the .ZIP file has been downloaded from NetApp’s web site and extracted. The VM has been launched within VMWare Workstation 7.1.3. A second VM with Windows XP is present and the NetApp System Manager application has been installed.
After the ONTAP VM is powered on, use option 4 within the initial main menu screen.
Enter “y” for the next two prompts. The system will then reboot.
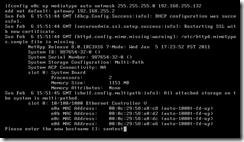
After the reboot has completed, the first prompt should be for the hostname.
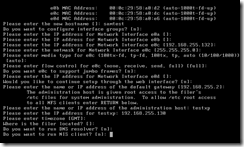
Most of the defaults can be used for the next several prompts. The administration host and the IP address (second VM running XP) were manually entered.
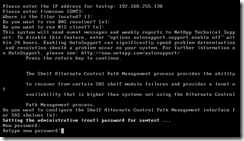
A new root password must be entered twice.
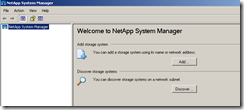
After a period of time, a password prompt should appear. At this point, the System Manager application can be used if desired. Upon launching the program, click on the Discover button.
Click on the Discover button within the dialog box and the ONTAP service should be found. Click on the Add Selected Systems button with the entry of the individual IP address highlighted.
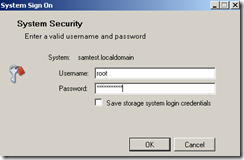
A dialog box should appear asking for the root password that was entered during the initial configuration of the ONTAP appliance.
All of the various management options should be available within the System Manger application.
The web interface of the ONTAP appliance should be available as well.
Tuesday, March 1, 2011
Ekahau HeatMapper
Ekahau HeatMapper is a free software tool for quick and easy coverage mapping of Wi-Fi (802.11) networks. HeatMapper uses your built-in wireless network adapter; all you need is a Windows-based laptop with wireless.
How to upgrade the free ESXi hypervisor to a new version
The steps below are concerning upgrading the free VMware ESXi hypervisor to a new version. The ESXi host in this example is within a VMware Workstation version 7.1.3 environment. The upgrade is from version 4.1 to version 4.1 Update 1.
The first component that is required is the VMware vSphere CLI product. This must be downloaded and installed. The hypervisor also must be placed into Maintenance Mode before performing the upgrade. All hosts running on the ESXi host should be shut down before performing this procedure.
Launch the vSphere client. Connect to the ESXi host in question. Right-click on the IP address of the ESXi host and select the “Enter Maintenance Mode” option. The command vicfg-hostops is another method to enter Maintenance Mode as well.
The following dialog box will appear. Verify all virtual machines running on the hypervisor are shut down and click the Yes button.
If the ESXi host is not within Maintenance Mode, the command to perform the upgrade will fail.
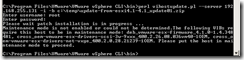
Access the CLI interface via the Start Menu and change to the bin subdirectory. Download the update and place it in a folder, such as TEMP in this example. Enter the following command:
perl vihostupdate.pl --server IP address of ESXi host –i –b Path to downloaded .ZIP file
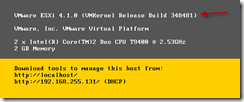
You should be prompted for the user name and password. The ESXi host will need to be rebooted once the process has completed. The new version should be visible via the main console screen.